Electrical Magnitudes, Units and Symbols
The physical magnitude is all that property that can be measured and its result expressed by a number that indicates its quantity based on one unit. These quantities can be multiples or submultiples of the unit and their values are represented in the International System with abbreviation and symbols.
On this page we show the fundamental physical quantities related to electrical science and engineering and the like, along with their units, abbreviation, symbols and basic calculations.
| Magnitud | Unit | Abbreviation | Symbol | Basic calculation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Electrical Basic Magnitudes |
||||
| Electric current | Amp | I | A | I = V / R V - voltage R - resistance |
| Voltage | Volt | V U |
V | V = R . I R - resistance I - electric current |
Resistive Magnitudes |
||||
| Electrical resistance | Ohm | R | 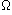 Omega |
R = V / I Ohm's law |
| Conductance | Siemens Mho |
G | 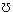 Inverted Omega |
G = 1 / R |
| Impedance | Ohm | Z | 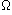 Omega |
|
| Resistivity | Ohm / meter / mm2 ( 20º) |
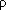 Ro |
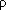 Ro |
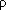 = Ohm / m / mm2 = Ohm / m / mm2 |
Capacitive Magnitudes |
||||
| Capacity | farad | C | F | C = load / voltage |
| capacitive reactance | Ohm | Xc | 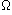 Omega |
Xc = 1 / pulsation . capacity |
| Coefficient lost capacitor | In decimal No. | d | d | d = Xc / Rp Rp = resistance losses |
| Capacitor quality factor | In decimal No. | Q | Q | Q = 1 / d |
| Dielectric Constant | Farad / meter | F / m | ||
Inductive Magnitudes |
||||
| inductance | Henry | L | H Hr |
L = flow / current |
| Inductive reactance | Ohm | Xl | 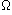 Omega |
XL = Pulsation / L |
| Coefficient lost coils inductors |
In decimal No. | d | d | d = R / XL |
| Quality factor of the coils inductors |
In decimal No. | Q | Q | Q = XL / R |
| Permeability | Henry / meter | H / m | ||
Electrical Signal magnitudes |
||||
| Frequency | Hertz | F | Hz | F = 1 / T T = period Frequency = Cycle |
| Wavelength | Meter | 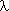 Landa |
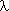 Landa |
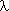 = Speed . frequency = Speed . frequency |
| Pulsation | 1 / seconds | 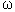 Minuscule omega |
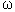 Minuscule omega |
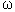 = 2 . Pi . Frequency = 2 . Pi . Frequency |
| Period | Seconds | T | T | T = 1 / F |
| Angular speed | Radian / Second | rad / s | Angular speed = rad / s | |
Electromagnetic Magnitudes |
||||
| Electrical load | Culombio | Q | Q | 1Q = 6.23.1018 electrons |
| Intensity of electrical field | Voltage / length | E | E | E = Voltage / length |
| Intensity of magnetic field | Gauss Ampere / meter |
H | H | H = MMF / length |
| Magnetomotriz forces | Gilbert Ampere - return |
MMF | 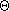 Theta |
MMF = I . No of turns |
| Magnetic flux | Weber Maxwell |
Wb M |
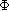 Phi |
Wb = V . Second |
| Magnetic induction | Tesla Gauss |
T G |
B | B = Magnetic flux / m2 |
Magnitudes of Electrical Work |
||||
| Electrical power | Watt | P | W | P = V . I |
| Current density | Ampere / mm2 | J | J | J = I / mm2 |
| Electrical work | Watt / second ( Joule ) |
W | Ws | W = Power . Time |
| Electrical performance | Decimal Nº % Percentage |
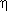 Eta |
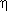 Eta |
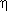 = P. output / P. consumption = P. output / P. consumption |
Ilumination magnitudes |
||||
| Luminous flow | Lumen | Lm | 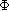 Phi |
|
| Luminous Intensity | Candela | cd | cd | |
| Luminous efficacy | Lumen / Watt | cd | 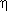 Eta |
cd = Lm / Watt |
| Lighting | Lux | Lx | E | Lx = Lm / m2 |
| Luminance | Candela / m2 | Cd / m2 | L | L = Cd / m2 |
Thermal Magnitudes |
||||
| Temperature | Degrees Celsius Degrees Fahrenheit Degrees Kelvin |
T | ºC ºF ºK |
|
| Heat quantity | Joule Kilocalorie |
J Kcal |
Q | 1 Kcal = 1000 cal = 4180 J |
| Calorific capacity | Joule / K Kilocalorie / K |
J / K Kcal / K |
K | |
| Thermal resistance | K / W | Rth | Rth | Rth = |
General Magnitudes in the Physics |
||||
| Time | Second | t | s | |
| Length | Meter | L | m | |
| Force | Newton | F | N | |
| Mass | Gram | m | g | |
| Energy | Joule | E | J | |
| Pressure | Pascal | P | Pa | |
| Sonority and logarithmic scales of power | Bel - Decibel | dB | dB | db = Bel / 10 |
Other Magnitudes |
||||
| Susceptance | Siemens | B | S | |
| Admittance | Siemens | Y | S | |
| Speed | Meter / Second | V | m / s | V = m / s |
| Speed of transmission of information |
Baud | bps | bps | bps = Bits . Second |